Alien Dictionary
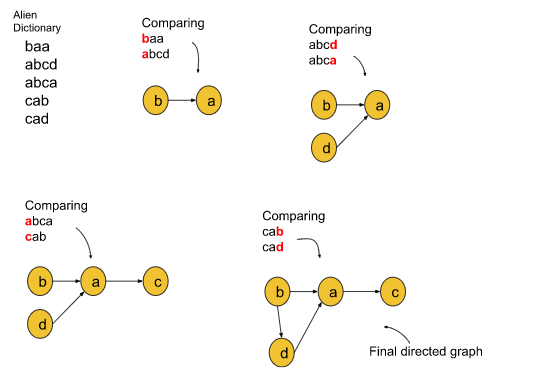
Alien Dictionary
INTRODUCTION:
The concept of an Alien Dictionary involves determining the lexicographic order of characters in an alien language based on a given list of words. In typical dictionaries, words are sorted based on alphabetical order. However, when dealing with an alien language, the character order might differ from the standard alphabetical sequence.
Understanding the Alien Dictionary:
- Unique Character Set:
- The alien language might contain a unique set of characters that don't follow the traditional English alphabetical order.
- The order of characters in this language might vary, leading to a different lexicographical order compared to standard dictionaries.
- Lexicographic Order:
- The task is to determine the correct order of characters in this alien language based on a given list of words.
- The order is established by analyzing the relationship between characters in adjacent words in the list.
- Character Dependencies:
- Comparing adjacent words reveals character dependencies and precedence.
- The order in which characters appear in words helps establish the relative order between characters in the language.
- Graph Representation:
- Constructing a directed graph where nodes represent characters and edges indicate precedence can help determine the character order.
- A topological sort on this graph reveals the lexicographic order of characters.
OVERVEIW:
-
Unique Character Set:
- The alien language comprises a distinct set of characters not following the traditional alphabetical order.
-
Determining Lexicographical Order:
- The objective is to discern the correct order of characters in this alien language based on observed words.
- The relative order of characters is inferred from the sequence of characters in adjacent words.
-
Character Dependencies:
- Examining adjacent words reveals character dependencies and precedence.
- Understanding the order in which characters appear in words aids in establishing their relative positions in the language.
-
Graph-Based Representation:
- Constructing a directed graph where nodes represent characters and edges indicate precedence can facilitate deducing the character order.
- Performing a topological sort on this graph unveils the lexicographical order of characters.
-
Handling Ambiguities:
- The provided word list might lack adequate information to ascertain a clear order for all characters.
- Ambiguities or inconsistencies within the input might result in an ambiguous or inconclusive order.
CODE:
from collections import defaultdict, deque def alienOrder(words): graph = defaultdict(set) in_degree = {c: 0 for word in words for c in word} # Build graph and compute in-degrees for i in range(len(words) - 1): w1, w2 = words[i], words[i + 1] for j in range(min(len(w1), len(w2))): if w1[j] != w2[j]: if w2[j] not in graph[w1[j]]: graph[w1[j]].add(w2[j]) in_degree[w2[j]] += 1 break if j == len(w2) - 1 and len(w1) > len(w2): return "" # Invalid input if shorter word is a prefix # Perform topological sort result = [] queue = deque([c for c in in_degree if in_degree[c] == 0]) while queue: char = queue.popleft() result.append(char) for nxt in graph[char]: in_degree[nxt] -= 1 if in_degree[nxt] == 0: queue.append(nxt) return ''.join(result) if len(result) == len(in_degree) else ""import java.util.*; public class AlienDictionary { public String alienOrder(String[] words) { Map<Character, Set<Character>> graph = new HashMap<>(); Map<Character, Integer> inDegree = new HashMap<>(); // Initialize in-degrees for (String word : words) { for (char c : word.toCharArray()) { inDegree.put(c, 0); } } // Build graph and compute in-degrees for (int i = 0; i < words.length - 1; ++i) { String w1 = words[i]; String w2 = words[i + 1]; for (int j = 0; j < Math.min(w1.length(), w2.length()); ++j) { if (w1.charAt(j) != w2.charAt(j)) { graph.computeIfAbsent(w1.charAt(j), k -> new HashSet<>()).add(w2.charAt(j)); inDegree.put(w2.charAt(j), inDegree.get(w2.charAt(j)) + 1); break; } if (j == w2.length() - 1 && w1.length() > w2.length()) { return ""; // Invalid input if shorter word is a prefix } } } // Perform topological sort StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <unordered_map> #include <unordered_set> #include <queue> std::string alienOrder(std::vector<std::string>& words) { std::unordered_map<char, std::unordered_set<char>> graph; std::unordered_map<char, int> in_degree; // Initialize in-degrees for (const std::string& word : words) { for (char c : word) { in_degree[c] = 0; } } // Build graph and compute in-degrees for (size_t i = 0; i < words.size() - 1; ++i) { const std::string& w1 = words[i]; const std::string& w2 = words[i + 1]; for (size_t j = 0; j < std::min(w1.size(), w2.size()); ++j) { if (w1[j] != w2[j]) { if (graph[w1[j]].find(w2[j]) == graph[w1[j]].end()) { graph[w1[j]].insert(w2[j]); ++in_degree[w2[j]]; } break; } if (j == w2.size() - 1 && w1.size() > w2.size()) { return ""; // Invalid input if shorter word is a prefix } } } // Perform topological sort std::string result; std::queue<char> q; for (const auto& entry : in_degree) { if (entry.second == 0) { q.push(entry.first); } } while (!q.empty()) { char c = q.front(); q.pop(); result += c; for (char nxt : graph[c]) { --in_degree[nxt]; if (in_degree[nxt] == 0) { q.push(nxt); } } } return (result.size() == in_degree.size()) ? result : ""; }EXPLANATION:
- Import Libraries:
- The
defaultdictfromcollectionsis used to create a default dictionary forgraphto store character dependencies. dequefromcollectionsis employed to create a double-ended queue for efficient popping and appending of elements.
- The
- Function Definition:
alienOrder(words)- This function takes a list of words and returns the lexicographical order of characters in an alien language.
- Initializing Data Structures:
graphis a defaultdict where each character maps to a set of characters it is dependent upon.in_degreeis a dictionary that tracks the in-degree (the number of incoming edges) for each character.
- Building the Graph and Computing In-degrees:
- Iterating through adjacent words, it finds the first character difference between two consecutive words.
- For each pair of adjacent words, it constructs the character dependencies based on the observed order.
- It populates
graphwith character dependencies and updates thein_degreeaccordingly.
- Performing Topological Sort:
- It initializes
resultto store the resulting order of characters. - Characters with no dependencies (in-degree of 0) are enqueued into the
queue. - While the
queueis not empty, it dequeues characters and explores their dependencies:- It decrements the in-degree of dependent characters and enqueues them if their in-degree becomes 0.
- The characters are added to the
resultin the order they are dequeued from the queue.
- It initializes
- Returning the Result:
- Finally, the function checks if the length of the resulting order (
result) matches the total number of characters (len(in_degree)). If they match, it returns the lexicographical order as a string; otherwise, it returns an empty string, indicating an invalid input.
- Finally, the function checks if the length of the resulting order (
TIME COMPLEXITY
- O(C) for constructing the graph + O(V + E) for topological sort.
- In the worst case, the overall time complexity is O(C + V + E), where C is the number of characters and V, E are related to the constructed graph.
SPACE COMPLEXITY
- O(C) for the character graph + O(V) for the queue/stack used in topological sort.
- In the worst case, the overall space complexity is O(C + V), where C is related to the characters and V to the constructed graph.
APPLICATIONS
- Deciphering Unknown Languages:
- When encountering unknown scripts or languages, understanding the order of characters aids in deciphering and translating texts.
- Historical Linguistics:
- Analyzing ancient texts or inscriptions where the script and language are unfamiliar often requires establishing character order.
Computer Science and Software Development:
- Compiler Design:
- Creating compilers or interpreters often involves handling different character sets and establishing order for parsing and lexical analysis.
- String Comparison and Sorting:
- In applications dealing with non-standard character orders, like in databases or file systems, understanding character precedence is crucial for sorting and comparison algorithms.
Genetics and Biology:
- Phylogenetic Analysis:
- In genetics, when analyzing DNA sequences or evolutionary relationships between species, character order determination is vital.
- Microbiological Studies:
- Studying microbial organisms or examining their genetic makeup might involve dealing with unconventional genetic codes that require character ordering.
Test Cases
Test Case 1: Input: "wrt", "wrf", "er", "ett", "rftt"
Output: wertf
Explanation: The input list of words is ["wrt", "wrf", "er", "ett", "rftt"]. The function alienOrder constructs a graph representing the ordering of characters based on the given words. It then performs a topological sort on the graph to find the lexicographically smallest order of characters. The output is "wertf", which represents the order in which the characters should appear.
Test Case 2:
Input: "z", "x"
Output: zx
Explanation: The input list of words is ["z", "x"]. The function alienOrder constructs a graph representing the ordering of characters based on the given words. It then performs a topological sort on the graph to find the lexicographically smallest order of characters. Since there are only two words and one character in each word, the order is straightforward. The output is "zx".
