Defanging an IP address
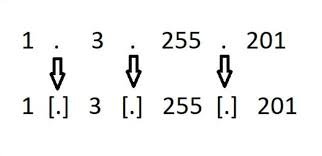
Defanging an IP address
Introduction:
Defanging an IP address refers to the process of modifying the standard format of an IP address to make it safe for use in contexts where raw IP addresses may be misinterpreted or misused. The term "defanging" is commonly used in the context of cybersecurity and programming to prevent accidental activation of hyperlinks or unintended actions when dealing with IP addresses.
In its typical format, an IP address consists of four sets of numbers separated by dots, such as "192.168.1.1." However, in certain situations, displaying or using the raw IP address directly can be problematic. For instance, in web development or online forums, an IP address written in its usual format can be automatically converted into a clickable link, leading to potential security concerns.
To mitigate this, defanging involves altering the IP address format to prevent automatic hyperlinking. A common method is to replace the dots with other characters, such as square brackets. For example, the IP address "192.168.1.1" would be defanged as "192[.]168[.]1[.]1."
By defanging an IP address, it becomes a plaintext representation that can be safely shared or displayed without triggering unintended actions. This practice is especially relevant in security-related discussions, documentation, or any scenario where clarity is crucial, and the risk of accidental interaction with the IP address needs to be minimized.
Algorithm:
- Initialize an empty string
defanged_ipto store the defanged IP address. - Iterate through each character of the input IP address.
- If the current character is a period (".")
- Append "[.]" to the
defanged_ipstring.
- Append "[.]" to the
- Otherwise
- Append the current character to the
defanged_ipstring.
- Append the current character to the
- Return the
defanged_ipstring.
Program in cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
// Function to defang an IP address
std::string defangIPaddr(std::string address) {
std::string defangedIP;
// Iterate through each character in the IP address
for (char c : address) {
// If the character is a dot '.', replace it with '[.]'
if (c == '.') {
defangedIP += "[.]";
} else {
// Otherwise, keep the character as it is
defangedIP += c;
}
}
return defangedIP;
}
int main() {
// Prompt the user to enter an IP address
std::string ipAddress;
std::cin >> ipAddress;
// Call the defangIPaddr function to defang the IP address
std::string defangedIPAddress = defangIPaddr(ipAddress);
// Display the defanged IP address
std::cout << defangedIPAddress << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Step-By-Step Explanation:
#
1. **Include necessary headers:** The program includes the necessary header files, `<iostream>` for input/output and `<string>` for string manipulation.
2. **Define `defangIPaddr` function:** This function takes an IP address as a string and returns the defanged IP address.
3. **Initialize `defangedIP` string:** This string will store the defanged IP address.
4. **Loop through each character:** The program uses a for-each loop to iterate through each character in the input IP address.
5. **Check if the character is a dot:** If the character is a dot '.', it is replaced with '[.]'. Otherwise, the character is appended to the `defangedIP` string.
6. **Prompt user for input:** In the `main` function, the user is prompted to enter an IP address.
7. **Call `defangIPaddr` function:** The entered IP address is passed to the `defangIPaddr` function.
8. **Display defanged IP address:** Finally, the defanged IP address is displayed to the user.
Compile and run the program, and it will defang the entered IP address. For example:
Input:
192.168.1.1
Output:
192[.]168[.]1[.]1
Program in python:
def defangIPaddr(address):
defanged_address = ""
# Iterate through each character in the original address
for char in address:
# Check if the character is a dot
if char == '.':
# If it's a dot, add "[.]" to the defanged address
defanged_address += '[.]'
else:
# If it's not a dot, simply add the character to the defanged address
defanged_address += char
# Return the defanged address
return defanged_address
ip_address = str(input())
defanged_ip_address = defangIPaddr(ip_address)
print(defanged_ip_address)
Step-By-Step Explanation:
-
Function
defangIPaddr:def defangIPaddr(address):: Define a function that takes anaddressparameter.defanged_address = "": Initialize an empty string to store the defanged IP address.
Inside the function:
- Use a
forloop to iterate through each character in the original address. - Check if the character is a dot (
.). - If it's a dot, append
"[.]"to the defanged address; otherwise, append the character itself. - Finally, return the defanged address.
-
Example Usage:
ip_address = "192.168.1.1": Define an example IP address.defanged_ip_address = defangIPaddr(ip_address): Call thedefangIPaddrfunction to get the defanged IP address.
-
Display the Result:
print(f"Original IP address: {ip_address}"): Display the original IP address.print(f"Defanged IP address: {defanged_ip_address}"): Display the defanged IP address.
-
Output:
Input:
192.168.1.1
Output:
192[.]168[.]1[.]1
Program in java:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DefangIPAddress {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Scanner object to read from standard input
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Read the IP address from the user
String ipAddress = scanner.nextLine();
// Defang the IP address
String defangedIPAddress = defangIPAddr(ipAddress);
// Display the defanged IP addresses
System.out.println(defangedIPAddress);
// Close the Scanner to release resources
scanner.close();
}
private static String defangIPAddr(String address) {
StringBuilder defangedAddress = new StringBuilder();
// Iterate through each character in the original address
for (char ch : address.toCharArray()) {
// Check if the character is a dot
if (ch == '.') {
// If it's a dot, add "[.]" to the defanged address
defangedAddress.append("[.]");
} else {
// If it's not a dot, simply add the character to the defanged address
defangedAddress.append(ch);
}
}
// Return the defanged address
return defangedAddress.toString();
}
}
Step-By-Step Explanation:
-
Class
DefangIPAddress:- A class is defined to encapsulate the program logic.
-
Method
defangIPaddr:public static String defangIPaddr(String address): Define a method that takes anaddressparameter and returns a defanged address as a string.StringBuilder defangedAddress = new StringBuilder();: Use aStringBuilderto efficiently build the defanged address.
Inside the method:
- Use a enhanced
forloop to iterate through each character in the original address. - Check if the character is a dot (
.). - If it's a dot, append
"[.]"to theStringBuilder; otherwise, append the character itself. - Finally, convert the
StringBuilderto a string and return the defanged address.
-
Method
main:public static void main(String[] args): The main method, representing the entry point of the program.
Inside the main method:
String ipAddress = "192.168.1.1";: Define an example IP address.String defangedIPAddress = defangIPaddr(ipAddress);: Call thedefangIPaddrmethod to get the defanged IP address.
-
Display the Result:
- Use
System.out.printlnto display the original and defanged IP addresses.
- Use
-
Output:
Input:
192.168.1.1
Output:
192[.]168[.]1[.]1
Space and Time complexities:
Time Complexity (C++):
- The function iterates through each character in the input address exactly once.
- The time complexity is O(n), where n is the length of the input address.
Space Complexity (C++):
- Additional space is used to store the defanged address in
defangedAddress. - The space complexity is O(n), where n is the length of the input address.
Time Complexity (Python):
- Similar to the C++ version, the function iterates through each character in the input address exactly once.
- The time complexity is O(n), where n is the length of the input address.
Space Complexity (Python):
- The
defanged_addressstring is used to store the defanged address. - The space complexity is O(n), where n is the length of the input address.
Time Complexity (Java):
- The function iterates through each character in the input address exactly once.
- The time complexity is O(n), where n is the length of the input address.
Space Complexity (Java):
- The
StringBuilder(defangedAddress) is used to efficiently build the defanged address. - The space complexity is O(n), where n is the length of the input address.
Real time Applications:
- Logging and Auditing:
- In log files and audit trails, IP addresses are often logged for tracking and analysis purposes. Defanging helps in preventing the accidental interpretation of these addresses as hyperlinks in log analysis tools or web interfaces.
- Security Analysis:
- When dealing with security events and incidents, analysts may need to share or document IP addresses. Defanging ensures that these addresses are human-readable and won't trigger unintended actions when shared in reports or communication.
- Web Application Security:
- In web applications, defanging is used to display IP addresses in a user-friendly manner. This is important to prevent potential security risks, such as injection attacks, that could be triggered if IP addresses are not properly sanitized before being displayed on a webpage.
- Email and Messaging Systems:
- In email systems or messaging applications, IP addresses might be part of the content. Defanging ensures that these addresses are not misinterpreted as links, helping to maintain the integrity of the message.
- Network Configuration Files:
- Defanging IP addresses is commonly employed in network configuration files where human-readable information is important. This makes it easier for administrators to review and manage the configurations without mistakenly activating a link.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing:
- In the context of threat intelligence sharing among security communities, defanging IP addresses can be a standard practice to prevent accidental execution of malicious actions when sharing information about potentially harmful addresses.
- Database Storage:
- In databases where IP addresses are stored, defanging can be applied to ensure that these addresses are not misinterpreted when queried or displayed in administrative interfaces.
- Regular Expressions and Text Processing:
- Defanging IP addresses is useful when dealing with regular expressions or text processing tasks. It prevents unintended matches when processing or searching through text containing IP addresses.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing:
- During vulnerability scanning and penetration testing, defanging is applied in reports to present findings in a readable and secure format, avoiding accidental execution of potentially harmful actions when reviewing the results.
- Network Traffic Analysis:
- In network traffic analysis tools or dashboards, defanging is used to display IP addresses in a user-friendly way, preventing confusion or unintentional actions during the analysis of network traffic patterns.
Defanging IP addresses is a common practice in various situations where human readability and security are important. It helps prevent accidental misinterpretation and ensures that information containing IP addresses is presented in a clear and safe manner.
Test Cases
- Input: 192.168.1.1
Output: 192[.]168[.]1[.]1
The given code reads an IP address from the user and replaces every period ('.') in the address with the string "[.]".
For example, given the input "192.168.1.1", the code produces the output "192[.]168[.]1[.]1".
This is achieved by iterating through each character of the input string. If the character is a period ('.'), it replaces it with "[.]", otherwise, it simply adds the character to the output string.
- Input: 10.0.0.2
Output: 10[.]0[.]0[.]2
The program reads the input IP address "10.0.0.2" from the user.
The defangIPAddr method is called with the input IP address.
Inside the defangIPAddr method, the string is iterated character by character. When encountering each character: If the character is a period ('.'), it's replaced with "[.]" and added to the defanged address. If the character is not a period, it's directly appended to the defanged address.
After iterating through all characters, the defanged address "10[.]0[.]0[.]2" is returned. Finally, the program prints the defanged IP address to the console. Therefore, the output "10[.]0[.]0[.]2" is obtained by replacing each period ('.') in the input IP address "10.0.0.2" with "[.]".
