Exploring Strings : LongestSubstringWithoutRepeating Characters
Exploring Strings : LongestSubstringWithoutRepeating Characters
Today, we dive into the fascinating world of Strings and uncover one of their most captivating mysteries . Get ready to embark on an adventure that will challenge your mind and leave you with newfound insights into Strings!
Introduction to strings
A string is a sequence of characters, typically used to represent text. Strings are one of the fundamental data types in many programming languages, including Python, Java, C++, and others.
- A string is a collection of characters, which can include letters, numbers, symbols, and white spaces.
- Strings are usually enclosed in single quotes (
') or double quotes ("), depending on the programming language.
Characteristics:
- Strings are immutable in many programming languages, meaning that once a string is created, its content cannot be changed.
- Operations on strings often include concatenation (joining two strings together), slicing (extracting a portion of a string), and searching for substrings.
Longest Substring Without Repeating
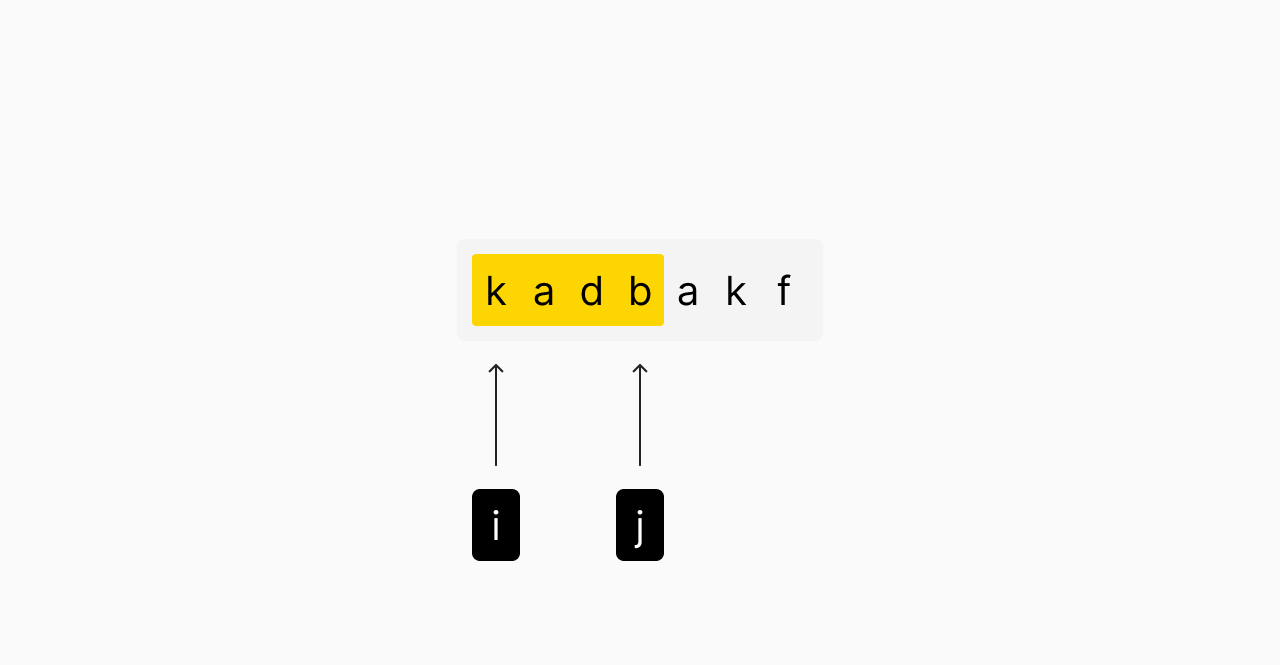
The longest substring without repeating characters problem involves finding the longest sequence of non-repeating characters in a given string
There are a few ways to solve this problem:
-
Brute force search
Check all the substrings of the given string and see if they contain unique or repeating characters.
-
Sliding window technique
Use two pointers and a dictionary to keep track of character counts. This avoids unnecessary computations and solves the problem in linear time.
-
Generate all substrings
Loop from the start of the string to its end index, and return the maximum length of all substrings with unique characters
Overview of strings
Declaration and Initialization:
- Strings can be assigned directly or constructed using various methods provided by the programming language.
Immutability:
- Strings are often immutable, meaning their content cannot be modified once they are created. Operations on strings usually return new strings.
Common Operations:
- Concatenation: Combining two strings.
- Slicing: Extracting a portion of a string.
- Length: Getting the length of a string
- Searching: Finding the position of a substring.
String Methods:
- Programming languages provide various built-in methods to manipulate strings, including upper( ), lower( ), strip( ), replace( ), and more.
Escape Characters:
- Strings may contain special characters or escape sequences, such as newline (\n), tab (\t), or a backslash ( \ ).
Code
# Copyrights to venkys.io
# For more programs visit venkys.io
# Python program for LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingCharacters
def lengthOFLongestSubstring(string : str) -> int:
start=end=ans=0
hashset=dict()
while end<len(string):
if string[end] not in hashset.keys():
hashset[string[end]]=end
end+=1
ans=max(len(hashset),ans)
else:
del hashset[string[start]]
start+=1
return ans
if __name__=="__main__":
s = int(input())#enter the substring
print(lengthOFLongestSubstring(s))#this prints the lenght of the longest substring
Explanation
Function to Find Length of Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters:
- Explanation:
- The function
lengthOFLongestSubstringtakes a string as input and returns an integer representing the length of the longest substring without repeating characters. - It uses a sliding window approach with a dictionary (
hashset) for character indexing. - The variables
start,end, andansare used to keep track of the current substring and the maximum length. - The
whileloop iterates through the string. - If a character is not in the hashset, it is added, and the length is updated.
- If a character is already in the hashset, the start index is updated.
- The maximum length is continuously updated.
- The function
3. Main Block:
- Explanation:
- The
if __name__ == "__main__":block ensures that the following code is executed only if the script is run as the main program, not when it's imported as a module. - The user is prompted to enter a string using
input. - Calls the
lengthOFLongestSubstringfunction with the input and prints the result.
- The
// Copyrights to venkys.io
// For more programs visit venkys.io
// Java program for LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingCharacters
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingChars {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// System.out.print("Enter a string: ");
String input = scanner.nextLine();
int result = lengthOfLongestSubstring(input);
System.out.println( result);
}
public static int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int n = s.length();
int maxLength = 0;
int start = 0;
HashMap<Character, Integer> charIndexMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int end = 0; end < n; end++) {
if (charIndexMap.containsKey(s.charAt(end))) {
// If the character is repeated, update the start index
start = Math.max(start, charIndexMap.get(s.charAt(end)) + 1);
}
// Update the character index in the map
charIndexMap.put(s.charAt(end), end);
// Update the maximum length
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, end - start + 1);
}
return maxLength;
}
}
Explanation
1**. Import Statements:**
- Explanation:
- Import statements include necessary Java libraries.
HashMapis used for efficient character indexing.Scanneris used for user input.
2**. Class Declaration:**
- Explanation:
- The class is named
LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingChars. - It is declared as
public, indicating that it can be accessed from outside the package.
- The class is named
3**. main Method:**
- Explanation:
- The
mainmethod is the entry point of the program. - It uses a
Scannerto take user input for a string. - Calls the
lengthOfLongestSubstringmethod with the input and prints the result.
- The
4**. lengthOfLongestSubstring Method:**
- Explanation:
lengthOfLongestSubstringmethod calculates the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.- It uses a sliding window approach with a HashMap (
charIndexMap) for character indexing. - The method returns the length of the longest substring.
// Copyrights to venkys.io
// For more programs visit venkys.io
// C++ program for LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingCharacters
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int n = s.length();
int maxLength = 0;
int start = 0;
unordered_map<char, int> charIndexMap;
for (int end = 0; end < n; end++) {
if (charIndexMap.find(s[end]) != charIndexMap.end()) {
// If the character is repeated, update the start index
start = max(start, charIndexMap[s[end]] + 1);
}
// Update the character index in the map
charIndexMap[s[end]] = end;
// Update the maximum length
maxLength = max(maxLength, end - start + 1);
}
return maxLength;
}
int main() {
// cout << "Enter a string: ";
string input;
getline(cin, input);
int result = lengthOfLongestSubstring(input);
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}
Explanation
1. Libraries and Namespace:
- Explanation:
- The code includes necessary C++ libraries for input/output (
iostream) and an unordered map (unordered_map) for efficient character indexing. using namespace std;is used to simplify the code by allowing the use of standard C++ identifiers without thestd::prefix.
- The code includes necessary C++ libraries for input/output (
2. Function to Find Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters:
- Explanation:
- The function
lengthOfLongestSubstringtakes a stringsas input and returns an integer representing the length of the longest substring without repeating characters. - It uses a sliding window approach with a hash map (
charIndexMap) to efficiently keep track of the indices of characters in the current substring. - The
startvariable represents the starting index of the current substring. - The loop iterates through the string from the beginning to the end.
- If a character is repeated, it updates the
startindex to be the maximum of the currentstartand the next index of the repeated character. - The character index is updated in the hash map.
- The maximum length is updated based on the length of the current substring.
- The final result is the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
- The function
3. Main Function:
- Explanation:
- The
mainfunction is the entry point of the program. - It prompts the user to enter a string using
coutand reads the input usinggetline. - It then calls the
lengthOfLongestSubstringfunction with the user-input string and prints the result usingcout.
- The
Time Complexity and Space Complexity
- Time Complexity : The time complexity is O(n), where n is the length of the input string. The while loop iterates through each character in the string once, and each iteration involves constant time operations. The deletion and insertion operations in the dictionary (hashset)are both O(1) on average.
- Space Complexity : The space complexity is also O(n), where n is the length of the input string. This is because the hashset dictionary can, in the worst case, contain all unique characters from the input string. The space used by the dictionary is proportional to the number of unique characters encountered during the iteration.
Real-World Applications
- Substring Matching in Text Processing:
- In text processing applications, finding the longest substring without repeating characters can be useful for identifying patterns or matching substrings efficiently. This is relevant in search engines, text editors, and data mining.
- Network Security:
- In network security, identifying patterns in network traffic can be crucial for detecting anomalies or potential security threats. Analyzing substrings without repeating characters can be part of the pattern recognition process.
- Genome Sequencing:
- In bioinformatics, the analysis of DNA sequences involves finding patterns and unique subsequences. Algorithms that deal with genome sequencing can benefit from efficient substring analysis to identify significant genetic information.
- Image Processing:
- Image recognition and processing often involve identifying unique patterns or shapes within an image. Techniques inspired by substring analysis can be used to efficiently process and recognize patterns in images.
- Speech Recognition:
- In speech recognition systems, analyzing acoustic signals may involve identifying recurring patterns or unique subsequences. Techniques inspired by substring analysis can aid in improving the accuracy of speech recognition algorithms.
Test Cases
Test Case 1:
Input:
abcabcbb
Output:
3
Explanation:
- The program prompts the user to input a string
"abcabcbb". - The
lengthOFLongestSubstringfunction is called with the input string. - Inside the function, a sliding window technique is used to find the longest substring without repeating characters.
- The window starts at the beginning of the string, and as characters are encountered, they are added to a dictionary
hashsetwith their indices. - If a character is encountered that is already in the
hashset, the window moves forward by removing the character at the start of the window until there are no repeating characters. - The length of the longest substring without repeating characters is returned as output. In this case, the longest substring is
"abc", which has a length of 3. Test Case 2: Input:
abbacd
Output:
3
Explanation:
- The program prompts the user to input a string
"abbacd". - The
lengthOFLongestSubstringfunction is called with the input string. - Inside the function, a sliding window technique is used to find the longest substring without repeating characters.
- The window starts at the beginning of the string, and as characters are encountered, they are added to a dictionary
hashsetwith their indices. - If a character is encountered that is already in the
hashset, the window moves forward by removing the character at the start of the window until there are no repeating characters. - The length of the longest substring without repeating characters is returned as output. In this case, the longest substring is
"bac", which has a length of 3.
