LINEAR SEARCH
LINEAR SEARCH
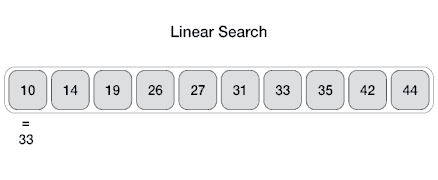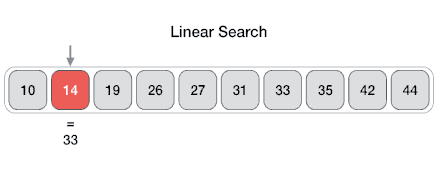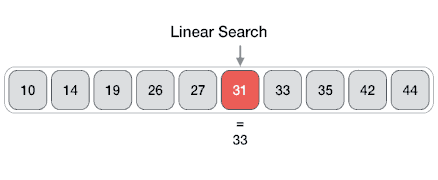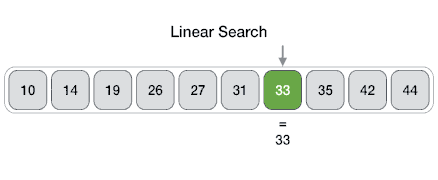
Linear search is like looking for a specific thing in a room by checking each item, one by one, until you find what you're looking for or realize it's not there.
Explanation Steps
(1) Think of a room filled with items (an array with elements).
(2) You're given a specific item you want to find in the room (the target element).
(3) You start looking from one side of the room (the beginning of the array).
(4) You check each item (element) one by one.
(5) For each item, you compare it with the one you're looking for.
(6) If you find the item you're looking for, you stop searching and say you found it.
(7) If you haven't found it, you keep checking the next items.
(8) You continue until you've checked every item in the room.
(9) If you found your item, you know where it is (the index in the array). If you checked everything and didn't find it, you know it's not there.
Advantages of linear search
- Simplicity
- Applicability
- Ease of Implementation
- Memory Efficiency
- Optimal for Small Lists
Drawbacks of Linear Search:
- Linear search has a time complexity of O(N),
- which in turn makes it slow for large datasets.
- Not suitable for large arrays.
use Linear Search :
- When we are dealing with a small dataset.
- When you are searching for a dataset stored in contiguous memory.
- Debugging and Verification
- User Interface (UI) Elements
- data Valdation
- Sequential File Search
- Online search Engines
Overview of Linear Search Algorithm
Linear search is a simple searching algorithm that sequentially checks each element in a list or an array until a match is found or the entire list has been traversed. It's also known as a sequential search.
Code for Linear Search in Pyhton, Java and C++
python
# Function to perform linear search in a list
def linear_search(array, element):
# Check for empty or None array
if array is None or not array:
print("Invalid input array")
return
# Iterate through the array to find the element
for idx, val in enumerate(array):
# If the element is found, print its index and exit the function
if val == element:
print(f"The element {element} found at index {idx} in the given array")
return
# If the element is not found in the array, print a message
print(f"The element {element} not found in the given array")
# Test list and target element
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
target = 10
# Perform linear search on the list for the target element
linear_search(arr, target)
Explanation of the Code
linear_search Function:
- Purpose:
The linear_search function is designed to search for a specific element within a list (array).
- Parameters:
It takes two parameters:
array: A list where the search will be conducted.
element: The target element that needs to be found in the list.
- Null or Empty List Check:
The function begins by checking whether the input list array is None or if it's an empty list. If either condition is true, it prints "Invalid input array" and returns from the function.
- Linear Search:
If the list is valid, it iterates through the list using a for loop and enumerate to get both index and value at each iteration.
For each value in the list, it checks if the current value (val) matches the target element (element).
If a match is found, it prints a message indicating the index at which the element is found in the list and exits the function.
- Result Messages:
If the loop completes without finding the element, it prints a message stating that the element was not found in the list.
- Testing the Function:
The code demonstrates the usage of the linear_search function by creating a list arr containing integers from 1 to 10 and setting a target element target to 10.
The linear_search function is called with these parameters (arr, target) to perform a search for the target element within the list.
Time Complexity and Space Complexity
- Time Complexity:
In the worst-case scenario, the linear search algorithm has a time complexity of O(n), where n is the number of elements in the list. This is because it might need to traverse the entire list to find the element or determine that it's not present.
The average and best-case time complexities are also O(n) since the search might terminate at any position in the list.
- Space Complexity:
The space complexity of the linear search algorithm is O(1) since it doesn't require any extra space proportional to the input size. It only uses a few variables for iteration and comparison.
JAVA CODE
public class LinearSearch {
// Function to perform linear search in an array
static void linearSearch(int[] array, int element) {
// Check for null or empty array
if (array == null || array.length == 0) {
System.out.println("Invalid input array");
return;
}
// Iterate through the array to find the element
for (int idx = 0; idx < array.length; idx++) {
// If the element is found, print its index and exit the function
if (array[idx] == element) {
System.out.printf("The element %d found at index %d in the given array%n", element, idx);
return;
}
}
// If the element is not found in the array, print a message
System.out.printf("The element %d not found in the given array%n", element);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test array and target element
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int target = 10;
// Perform linear search on the array for the target element
linearSearch(arr, target);
}
}
Explanation of the Code
LinearSearch Class:
- linearSearch Method:
Purpose: The linearSearch method is responsible for performing a linear search in an array to find a particular element.
Parameters: It takes in two parameters:
array: An integer array where the search will be conducted.
element: The target element that needs to be found in the array.
- Null and Empty Check:
It starts by checking whether the input array array is null or if its length is 0 (indicating an empty array). If either condition is true, it prints
"Invalid input array" and exits the method.
- Linear Search:
If the array is valid, it iterates through the array using a for loop.
For each element in the array, it checks if the current element (array[idx]) matches the target element (element).
If a match is found, it prints a message indicating the index at which the element is found in the array and exits the method.
- Result Messages:
If the loop completes without finding the element, it prints a message stating that the element was not found in the array.
- main Method:
Testing the linearSearch Method:
In the main method, there's a test scenario set up:
An array arr containing integers from 1 to 10 is created.
A target element target is set to 10.
linearSearch is called with these parameters (arr, target) to perform a search for the target element within the array.
C++ Code
'''
#include <iostream>
// Function to perform linear search in an array
void linearSearch(int arr[], int size, int element) {
// Check for null array or non-positive size
if (arr == nullptr || size <= 0) {
std::cout << "Invalid input array" << std::endl;
return;
}
// Iterate through the array to find the element
for (int idx = 0; idx < size; idx++) {
// If the element is found, print its index and exit the function
if (arr[idx] == element) {
std::cout << "The element " << element << " found at index " << idx << " in the given array" << std::endl;
return;
}
}
// If the element is not found in the array, print a message
std::cout << "The element " << element << " not found in the given array" << std::endl;
}
int main() {
// Test array and target element
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int target = 10;
// Perform linear search on the array for the target element
linearSearch(arr, size, target);
return 0;
}
'''
Explanation of the Code
- linearSearch Function: Purpose: The linearSearch function is designed to perform a linear search within an array to find a specific element. Parameters: It takes in three parameters: arr[]: An integer array where the search will be conducted. size: The size of the array. element: The target element that needs to be found in the array.
- Null and Size Check: It starts by checking whether the input array arr is nullptr (i.e., null in C++) or if the size of the array is non-positive. If either condition is true, it prints "Invalid input array" and exits the function.
- Linear Search: If the array is valid, it proceeds to iterate through the array using a for loop. For each element in the array, it checks if the current element (arr[idx]) matches the target element (element). If a match is found, it prints a message indicating the index at which the element is found in the array and exits the function.
- Result Messages: If the loop completes without finding the element, it prints a message stating that the element was not found in the array.
- main Function: Testing the linearSearch Function: In the 'main' function, there's a test scenario set up: An array 'arr' containing integers from 1 to 10 is created. The size of the array is calculated using 'sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0])', which determines the number of elements in the array. A target element 'target' is set to 10. 'linearSearch' is called with these parameters ('arr', 'size', 'target') to perform a search for the target element within the array.
Real-world Applications
- Database Operations: Linear search can be used in databases for basic search operations on unsorted datasets. Finding Elements in Lists or Arrays: It's applicable in scenarios where finding a specific element in a collection of data is required.
- Simple Search Operations: Linear search can be applied in various programming scenarios where a basic search operation is needed and the dataset isn't too large.
- Handling Small Lists or Arrays: It's efficient for small lists or arrays where the overhead of implementing complex search algorithms might not be justified. Linear search, although straightforward, serves as a fundamental algorithmic concept and is often used as a starting point for understanding more complex searching algorithms.
