Linked List
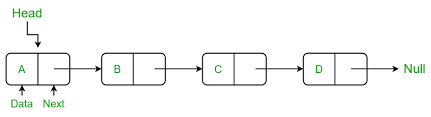
Linked Lists
Linked lists will be introduced using an example. Suppose a brokerage firm maintains a file where each record contains a customer’s name and salesperson, and suppose the file contains the data appearing in the figure below. The file could be stored in the computer by such a table, i.e., by two columns of nine names. However, as the following discussion shows, this may not be the most helpful way to store the data.
|
|
Customer |
Salesperson |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
Adams Brown Clark Drew Evans Farmer Geller Hill Infeld |
Smith Ray Jones Ray Smith Jones Ray Smith Ray |
One way of storing the data is to have a separate array for sales representatives and an entry (called a pointer in C/C++ programming language) in the customer file that tells you where each customer’s sales representative is. The arrows in the figure below show some of the pointers pointing to where they point. Continuing with this representation, an integer as a pointer would use less space than a name, meaning it would save even more space, especially if there are lots of customers per salesperson.


