Min Heap Sort Algorithm
Optimizing Sorting Efficiency: Min Heap Sort Algorithm
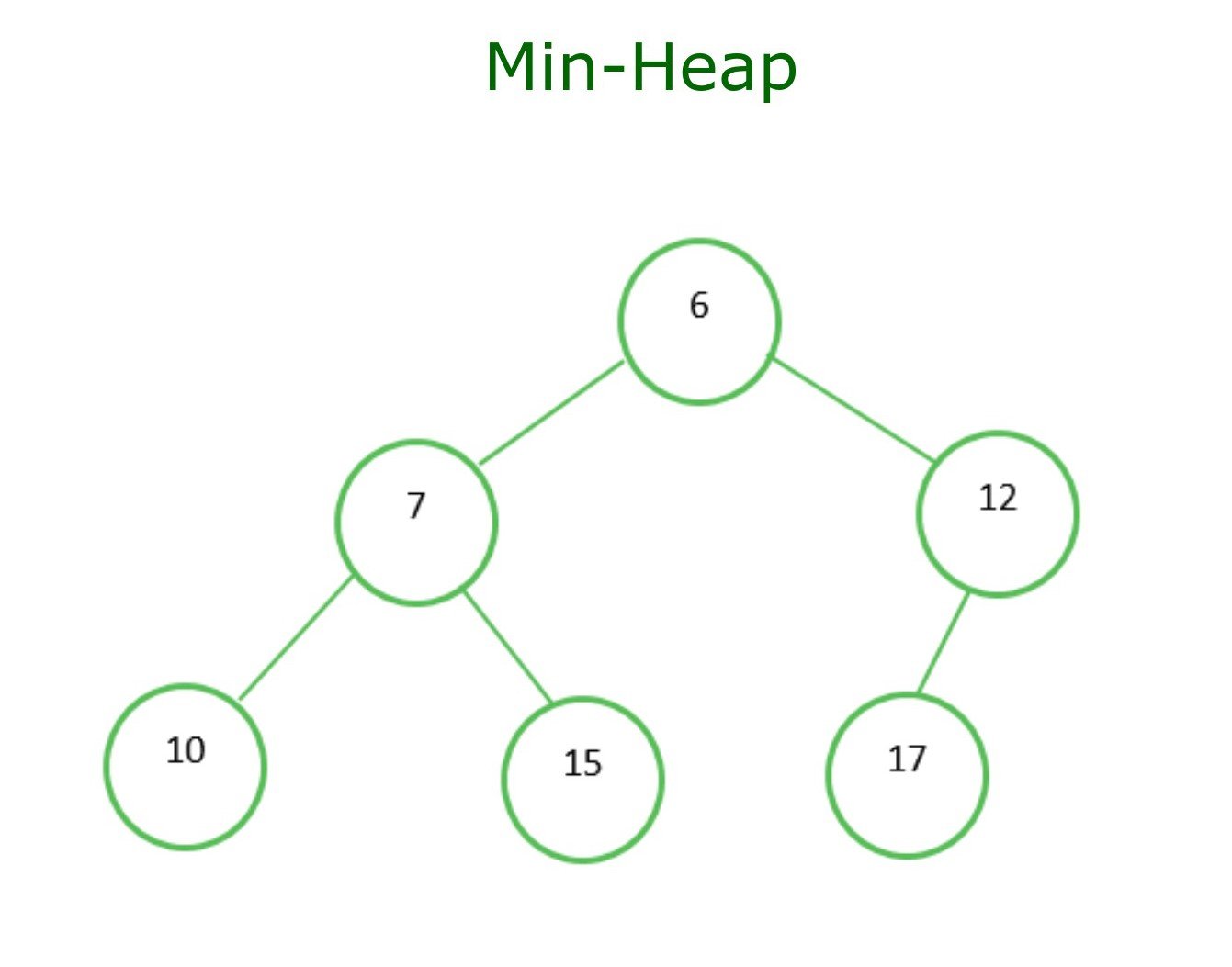
Today, let's explore the world of Sorting algorithms, which play a pivotal role in computer science, facilitating the arrangement of elements in a specific order for efficient data retrieval and manipulation. Among the diverse array of sorting techniques, Min-Heap Sort stands out as a versatile and resource-efficient method.
Introduction
Min Heap Sort, also known as Heap Sort, is a comparison-based sorting algorithm that uses a binary heap data structure to build a special kind of binary tree called a min-heap.
A min-heap is a binary tree data structure where the value of each node is less than or equal to the values of its children and the tree is complete (all levels are filled, except possibly for the last level, which is filled from left to right). In the context of heap sort, the heap is represented as an array. Min Heap Sort is a sorting algorithm that utilizes the min-heap data structure to efficiently sort an array in ascending order.
Build Heap
Building a Min Heap involves rearranging an array to satisfy the Min Heap property. The first step is to visualize the array as a binary tree. The array elements are the nodes of the tree, and their indices determine the relationships between nodes. For example, Consider the array
arr = [4, 10, 3, 5, 1]
The binary tree representation looks like this:
4
/ \
10 3
/ \
5 1
Then Identify the Last Non-Leaf Node For an array of size 'n', the last non-leaf node is at index '(n/2 - 1)'. In our case, 'n' is 5, so the last non-leaf node is at index '(5/2 - 1) = 1'. Therefore, we start our heap construction from index 1.
Now Heapify Each Node Starting at Index 1 (Node with value 10) Heapify the node at index 1. Compare it with its children (indices 3 and 4) and swap with the smallest child if necessary.
Before heapify
4
/ \
10 3
/ \
5 1
After heapify
4
/ \
1 3
/ \
10 5
Starting at Index 0 (Node with value 4) Heapify the node at index 0. Compare it with its children (indices 1 and 2) and swap with the smallest child if necessary.
Before heapify:
4
/ \
1 3
/ \
10 5
After heapify:
1
/ \
4 3
/ \
10 5
After completing the heapify process for each non-leaf node, the array 'arr' is transformed into a Min Heap, where the value of each node is less than or equal to the values of its children.
1
/ \
4 3
/ \
10 1
sorting
-
Once the array is converted into a Min Heap, the smallest element (located at the root) is swapped with the last element in the array. we can also call Extraction of Minimum Element.
-
This element is considered sorted and is removed from further consideration. The heap property is then restored by heapifying the reduced heap.
-
Repeat the extraction and heapify process until the Min Heap is empty. Append the extracted elements to the sorted array.
Python Code
#Copyrights to vsdevelopers.io
#For more programs visit vsdevelopers.io
#Python program for Heap sort using max Heap
# Function to maintain max heap properties
def VSDminHeapify(arr,size,i):
#Declare the current element index as smallest
small=i
#Find the index of leftchild element
leftchild=(2*i)+1
#Find the index of rightchild element
rightchild=(2*i)+2
#Check the smallest element between leftchild and current element
if leftchild<size and arr[i]<arr[leftchild]:
small=leftchild
#Check the smallest element between rightchild and smallest element
if rightchild<size and arr[small]<arr[rightchild]:
small=rightchild
# If smallest element is not current element
# Swap the smallest element and current element
# Heapify the current array
if small!=i:
arr[small],arr[i]=arr[i],arr[small]
VSDminHeapify(arr,size,small)
# Function to sort the given array using minheap in descending order
def VSDMinheapsort(array):
size=len(array)
# Heapify the given array into min heap
for i in range((size//2)-1,-1,-1):
VSDminHeapify(array,size,i)
# Find the min element in array
for i in range(size-1,-1,-1): # Decrease the last index by 1
# Swap the min element with last index element
array[0],array[i]=array[i],array[0]
# Heapify the current array upto last index
VSDminHeapify(array,i,0)
#Fucntion to print array
def printarray(array):
for i in array:
print(i,end=" ")
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Get user input for the array
input_str = input("Enter elements of the array separated by spaces: ")
# Convert the input string to a list of integers
arr = [int(x) for x in input_str.split()]
# Perform min heap sort on the array
VSDMinheapsort(arr)
# Print the sorted array
print("Sorted array using minheapsort:")
printarray(arr)
Java code
/* Copyrights to vsdevelopers.io */
/* For more programs visit vsdevelopers.io */
/* Java program for Heap sort using min Heap */
// Class to hold the structure of a node in a tree
public class VSDMinHeapSort {
public static class Node {
int data; // Holds the value of the node
Node left; // Holds the left pointer of the node
Node right; // Holds the right pointer of the node
// Default constructor
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
// Root node
public static Node root = null;
// Variables to hold count of left and right nodes, and other information
public static int leftcount = 0;
public static int rightcount = 0;
public static int deletecount = 0;
public static Node deletenode = null;
public static Node parent = null;
// Method to build Heap along with the maintenance of the complete binary tree
public static Node VSDbuildHeap(Node root, Node newNode) {
if (root == null) root = newNode; // If the root is null, set it as the new node
else if (root.left != null && root.right != null) {
// If both left and right children are present for the root
leftcount = VSDsubtreeCount(root.left); // Get left nodes count from the left of the current root
rightcount = VSDsubtreeCount(root.right); // Get right nodes count from the right of the current root
int height = VSDfindHeight(root); // Get height of tree
// Checking for the correct position to insert
if (leftcount < (VSDexpectedCount(height) / 2)) {
VSDbuildHeap(root.left, newNode);
} else if (leftcount == rightcount)
VSDbuildHeap(root.left, newNode);
else
VSDbuildHeap(root.right, newNode);
} else if (root.left == null) {
root.left = newNode; // If left child is null, set the new node as the left child
} else if (root.right == null) {
root.right = newNode; // If right child is null, set the new node as the right child
}
return root;
}
// Function to maintain min heap properties
public static Node VSDHeapify(Node current) {
if (current.left != null)
current.left = VSDHeapify(current.left);
if (current.right != null)
current.right = VSDHeapify(current.right);
if (current.left != null && current.left.data < current.data) {
// Swap if the left child has a smaller value
int temp = current.left.data;
current.left.data = current.data;
current.data = temp;
}
if (current.right != null && current.right.data < current.data) {
// Swap if the right child has a smaller value
int temp = current.right.data;
current.right.data = current.data;
current.data = temp;
}
return current;
}
// Function to return the expected node count for a given height
public static int VSDexpectedCount(int h) {
int count = 0;
while (h >= 0) {
// Calculate the expected count using the formula for a complete binary tree
count += Math.pow(2, h);
h--;
}
return count;
}
// Function to return the node count for a given subtree
public static int VSDsubtreeCount(Node current) {
int leftheight = 0; // Variable to hold the height of the left subtree
int rightheight = 0; // Variable to hold the height of the right subtree
// Traversing to the left subtree to find the minimum height
if (current.left != null) {
leftheight = VSDsubtreeCount(current.left);
}
// Traversing to the right subtree to find the minimum height
if (current.right != null) {
rightheight = VSDsubtreeCount(current.right);
}
// Selecting the minimum height and adding 1 for the root's height
int count = rightheight + leftheight + 1;
return count;
}
// Function to return the height of the tree
public static int VSDfindHeight(Node current) {
if (current == null)
return -1; // Return -1 for an empty subtree
else {
int lh = VSDfindHeight(current.left);
int rh = VSDfindHeight(current.right);
// Return the maximum of left and right subtree heights, plus 1 for the current node
if (lh > rh)
return (lh + 1);
else
return (rh + 1);
}
}
// Function to display elements in the min heap using inorder traversal
public static void VSDinorder(Node root) {
if (root.left != null) VSDinorder(root.left);
System.out.println(root.data);
if (root.right != null) VSDinorder(root.right);
}
// Function to choose the most recently inserted element based on count
public static void VSDchooseNode(Node current, int level, int size) {
if (current == null) {
return;
}
if (level == 0) {
// Increment deletecount based on the level of the tree
deletecount++;
if (deletecount == size / 2) {
parent = current; // Set the parent when deletecount reaches half of the size
}
if (deletecount == size) {
deletenode = current; // Set the deletenode when deletecount reaches the size
return;
}
} else if (level > 0) {
// Recursively move to the next level
VSDchooseNode(current.left, level - 1, size);
VSDchooseNode(current.right, level - 1, size);
}
}
// Function to delete the root node from the heap
public static Node VSDdeleteNode(Node root, int height, int size) {
// Obtain the correct child node to replace with the root
for (int i = 0; i <= height; i++) {
VSDchooseNode(root, i, size);
}
int temp = root.data;
root.data = deletenode.data;
deletenode.data = temp;
// Deleting the node by setting its parent's left or right child to null
if (parent.right != null) parent.right = null;
else parent.left = null;
// Calling heapify to maintain min heap properties
root = VSDHeapify(root);
return root;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] arr = new int[]{10, 11, 13, 6, 25, 17, 12, 5, 4};
Node n;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
n = new Node(arr[i]);
root = VSDbuildHeap(root, n);
// Calling function to maintain min heap properties
root = VSDHeapify(root);
}
System.out.println("Insertion");
// Display elements after insertion
// Variable to hold the number of elements in the heap
int size = arr.length;
System.out.println("The ascending order is:");
while (size > 1) {
// Reset deletecount for each deletion
deletecount = 0;
// Print the root data (min value in the heap)
System.out.println(root.data);
int height = VSDfindHeight(root);
// Delete the root and maintain min heap properties
root = VSDdeleteNode(root, height, size);
// Decrease the size of the heap
size--;
}
// Print the last remaining element in the heap
System.out.println(root.data);
// Set the root to null, freeing the memory
root = null;
}
}
Let us see the step-by-step process of solving the anagram finder using the Hash Table in (JAVA)
-
Node Class The first step is to define a basic structure for a node in a binary tree. Each node has an integer value (data) and pointers to its left and right children.
-
Global Variables Next define global variables which are used to maintain information and state throughout the program. They store the root of the tree, counts of left and right nodes, counts for deletion, and references to nodes during deletion.
-
buildHeap Right after defining global variables build min heap which maintains a complete binary tree structure. It inserts a new node into the tree and ensures that the heap properties are maintained. It first checks if the tree is empty and, if so, sets the new node as the root. If the tree is not empty, it checks whether both left and right children are present at the root. If yes, it determines the correct position to insert the new node based on the counts of nodes in the left and right subtrees. If only the left or right child is present, the new node is inserted accordingly.
-
Heapify Next is to build a heapify method to ensure that the min-heap property is maintained after each insertion. It recursively traverses the tree and swaps nodes to maintain the property. It starts by recursively heapifying the left and right subtrees. Then, it checks if swapping is necessary for the current node with its left and right children to ensure that the smallest value is at the root. The recursive approach ensures that the entire tree is transformed into a min-heap.
-
ExpectedCount This method calculates the expected count of nodes for a complete binary tree with a given height using the formula for the sum of a geometric series. It uses a while loop to iteratively calculate the count of nodes at each level and adds them to the total count. The loop continues until it reaches the root level (height zero). The final total count represents the expected number of nodes in a complete binary tree with the specified height.
This method is crucial for determining the correct position to insert a new node in the VSDbuildHeap method based on the counts of nodes in the left and right subtrees. It ensures that the tree remains complete and follows the properties of a binary heap.
-
subtreeCount Recursively calculates the count of nodes in a subtree rooted at a given node('current'). It does this by recursively finding the heights of the left and right subtrees and then summing these heights along with 1 for the current node. It determines the correct position to insert a new node in the VSDbuildHeap method based on the counts of nodes in the left and right subtrees. It contributes to maintaining the complete binary tree structure.
